How digital badges can improve business performance
Digital badges have gained increasing recognition as micro credentials and pedagogical tools over the last decade.
Digital badges serve as a practical way to engage with employees and recognize accomplishment as part of an online program and they can also be useful in creating awareness among colleagues, potential employers or managers of new professional skill sets or achievements.
In our previous article « Digital Badges: why they are important for engagement? » published a few weeks ago, we already talked about how digital badges changed the logic of the certification process, both in an educational context and in professional organisations.
Now we would like to talk more about how digital badges can be applied to improve business performance.
How can they contribute to improving business performance and how they can change employees’ behaviour?
Let’s start with the educational system
For example, since 2000 the City & Guilds of London Institute has awarded more than 20 million vocational qualifications and has recently begun exploring the potential of digital credentials to provide independent, verifiable evidence of attainment. Another awarding body that has already embraced digital based certification is Pearson Education. Pearson supports over 75 million learners in schools, colleagues and in employment but only a handful of its qualifications have so far been transitioned to digital credentialing[2].
Just as the name implies, digital badges are digitalized symbols that represent and communicate achievements.
But why they are so innovative? Where is their added value?
What makes this type of technology unique and valuable in education is that a digital badge includes important credentialing and learning metadata, such as the badge issue date and authority, criteria to demonstrate the accomplishment of a skill or acquisition of specific knowledge, duration of credential effectiveness and endorsement information.
But at the same time there are also risks involved.
While the Open Badges standard ensures portability of the meta-data, it does not define a hierarchical taxonomy of knowledge, skills, behaviour and experience (i.e. a competence model) for any subject domain certified by the badge.
Today this constitutes the biggest problem we encounter in using digital badges to certify skills in academia or business. How readily will the certification be recognised? Will there be a legal authority endorsed to assume responsibility for certification?
Will the biggest questions centre around the relevance of the issuer? Will the issuer brand be sufficiently trustworthy to take responsibility for the quality of the certified skills?
While many open questions still have to be answered, today digital badges are successfully used in education to improve performance in learning.
Broadly speaking, according to Cheng and colleagues[3], there are four different types of DBs used in education:
- Candy badges for positive reinforcements
- Recognition badges to endorse accomplishments
- Credential badges to certify qualifications
- Instructional badges that serve as a micro-learning platform and a content management system.
And above all, studies have found evidence of positive impact from using DBs as credentials to recognize and document achievement. Learner engagement and participation increased when DBs were used to accord recognition and rewards for the attainment of specific levels of performance.
Today digital badges already constitute an important opportunity for institutions and companies to implement actively in the educational sector.
The next step will regard competence models that are required to attribute even more value to this approach. At the moment, this challenge has not yet been fully solved in the offline (real) world. The wide range of different ranking systems aimed at evaluating universities across the globe, still makes it difficult to obtain a final answer about the value of an achievement/degree certified (offline, on paper) by a university/institution. But this challenge applies equally across the educational field, both online and offline.
At the same time, business have been using digital badges to improve organizational performance and employee engagement.
And what about the business sector?
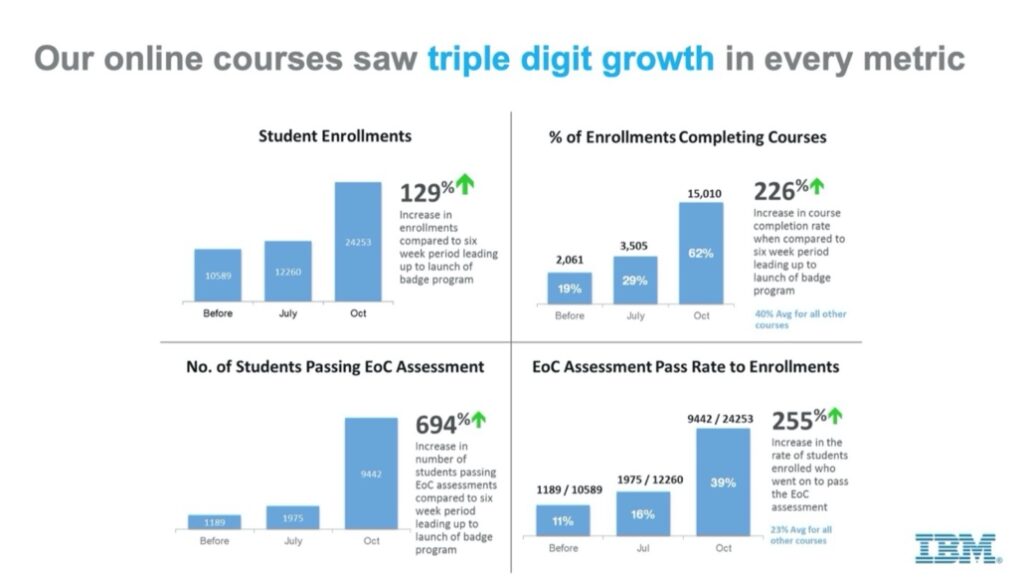
In the summer of 2014, IBM began to explore the value of digital badges for a single use case: How could the engagement of software developers be increased while they were using data products? The problem was about an internal skill development platform: site traffic was fairly good, but students were not completing courses and taking the final exams. What if we introduced digital badges as an incentive to encourage engagement?[4]
A few weeks after the launch of the Digital Badge Program, results were already significant:
- Student enrollments increased by 129%
- The percentage of enrollees who actually completed courses increased by 226%.
- The number of students passing the end of course exam increased by 694% compared to the six-week period leading up to the introduction of digital badges. It’s important to note there were no other contributing factors to this success, like promotions or announcements by IBM executives.
And even sales performances have been improved by the digital badges program.
3 benefits from implementing digital badges
In recent years another interesting business application has emerged from Joe Cannata, the Certification Director forKinaxis, a SaaS company that produces RapidResponse, an enterprise planning and supply chain platform that helps companies manage their supply chains[5].
The Kinaxis badging program has been offered to Kinaxis staff, Kinaxis’s customers and those who work for its extended enterprise, as well as consultants in partner companies, who carry out implementation work for the companies that are ultimately using the software.
According to Joe Cannata, the benefit of the badge over a paper certificate is that « the certificate doesn’t tell the full story; the digital badge does », Joe suggests. « A digital badge is a representation of achievement backed by a set of skills and a route to earn those skills and with verifiable metadata, including who issued it, when, and how long it’s valid. »
By leveraging results obtained at Kinaxis, we can summarise 3 benefits from implementing digital badges:
- When someone earns a digital badge, ad hoc posts are shared on LinkedIn by the company’s leadership. Those posts are liked and shared by others inside and outside the company which magnifies the impact of the achievement while also amplifying the company name and its certifications out into the world.
- Customers looking to hire a company will take into account the number of credential holders a given implementation provider has. « In the old days, customers would ask for the resumes of consultants for a project. The number of people certified, and to which level, is definitely a factor which influences customer’s decisions on which partner to choose. » Now it’s badges. Customers « adopt the same approach as a recruiter. »
- Digital badges are the preference of new generations of workers. This is about habits, identities and digital skills. Young employees and consultants lead digital lives and they use digital media to share content and to broadcast about themselves.
« Paper and PDF certificates are yesterday, in the room with the fax machines.»
Joe Cannata
Let us help you
[1] Header photo by Lucian Alexe on Unsplash
[2] Jagger, P. D. (2019). Digital Badging: Is it Worth IT? ITNOW, 61(4), 54–55. https://doi.org/10.1093/itnow/bwz114
[3]Cheng, Z., Richardson, J. C., & Newby, T. J. (2020). Using digital badges as goal-setting facilitators: a multiple case study. Journal of Computing in Higher Education, 32(2), 406–428. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12528-019-09240-z
[4] Leaser, D. (2019). Do digital badges really provide value to businesses? IBM Training and Skills Blog. https://www.ibm.com/blogs/ibm-training/do-digital-badges-really-provide-value-to-businesses/
[5] Jennifer Jones, How Digital Badging Drives Learner Engagement and Improves Business Performance. Retrieved March 9, 2021, from https://www.thoughtindustries.com/blog/how-digital-badging-drives-learner-engagement-and-improves-business-performance
WANT TO RECEIVE OUR LATEST THOUGHT LEADERSHIP CONTENT?









